 2023 appears to be a year of technological innovation for solar modules. Two trends in particular are expected to determine production in the industry: First of all, there will be improved efficiency thanks to the increasing use of n-type M10 solar cells. In addition, higher capacity is to be expected, with a particular focus on weight and size.
2023 appears to be a year of technological innovation for solar modules. Two trends in particular are expected to determine production in the industry: First of all, there will be improved efficiency thanks to the increasing use of n-type M10 solar cells. In addition, higher capacity is to be expected, with a particular focus on weight and size.
Today, the most widely used technology for high-efficiency modules is still the PERC cell (p-type), especially the Half-Cut Multi-Busbar version. However, a trend reversal is expected as early as 2023 and TOPCon technology in the form of the n-type cell will become more widespread.
Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute have developed a series of cost-oriented strategies to accelerate the industrial production of TOPCon (tunnel oxide passivated contacts) solar products:
In the article “TOPCon – Technology options for cost-efficient industrial manufacturing”, published in Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, the German research team explains that the existing processes and systems, which are usually used to manufacture PERC cells, can be easily adapted to the production of TOPCon cells by the addition of two process steps. This requires the creation of an oxide layer and the application of inherent/doped polysilicon.
With the new n-type technology, the products achieve greater capacity and nominal output, are more powerful, more productive and longer-lasting with the same area requirement, and have lower electricity production costs.
Here is an overview of the advantages of TOPCon technology:
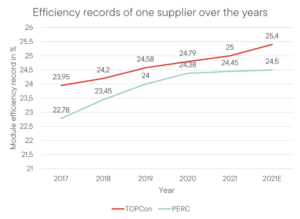
In recent years, TOPCon cells have achieved greater efficiency than PERC cells, ranging from 28.2% to 28.7% last year. As a result, power generation is higher due to smaller losses, more current/voltage, negligible LID and LeTID degradation, and lower temperature coefficients.
Low temperature coefficients
Lower temperature coefficients lead to improved module production performance.
 The productivity increase in normal operation is 2 to 3%.
The productivity increase in normal operation is 2 to 3%.
This makes the modules particularly suitable for systems with reeduced ventilation, such as on the roofs of industrial buildings.
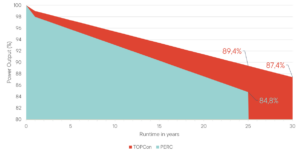
Reduced linear degradation and extended performance guarantee
In addition to the product warranty, which, for example, is 15 years for IBC SOLAR modules, the linear work performance guarantee is also a decisive factor, which is not 25, but 30 years for n-type modules.
Lower power losses over the entire service life of the module ensure higher production with longer operating times.
Best performance with low irradiation
N-type cells not only have a longer lifespan, but also greater capacity in low-sun radiation, i.e. in the early hours of the morning and at sunset.
 This means, for example, that you have more hours per day to use or store solar energy for self-consumption.
This means, for example, that you have more hours per day to use or store solar energy for self-consumption.
Another indication that n-type technology is likely to continue to prevail is the planned expansion of production lines by leading manufacturers.
While n-type technology is spreading rapidly at cell level, there is a significant trend towards the M10, measuring 182 × 182 millimetres, which, in 2023, is expected to overtake the M6, measuring 166 × 166 millimetres. The biggest advantage of the M10 wafers is that they can provide more capacity over the same area and thus bring advantages in terms of production, reliability, transport and installation.
Of course, we at IBC SOLAR also have modules with n-type technology in our portfolio. These can be found here and here.
So there is movement in the modules sector and we are already looking forward to seeing what else 2023 will bring in this regard.